Beijing Temperatures: Monthly Averages and Year-Round Insights
On this page, we’ll explore temperature statistics for Beijing in Beijing Area, China, including day and night variations and monthly averages. We’ll also compare the annual temperature to other cities in China.
Monthly Temperature Averages
Depending on the time of the year, temperatures range from very warm to cold in Beijing. Typically, maximum daytime temperatures range from a very warm 34°C in July to a chilly 3°C in the coolest month, January. Nights are cooler, with temperatures generally dropping to -8°C, particularly during the colder months.
The chart below illustrates the average maximum day and minimum night temperatures in Beijing by month:
The early hours of 4 AM to 6 AM often see the lowest temperatures, while 3 PM marks the peak of the day’s heat as the sun’s impact is strongest. July, the city’s warmest month, boasts 195 hours of sunshine.
The chart below shows the average temperature throughout the year:
January, the city’s coldest month, sees about 4 mm of rainfall spread over roughly 2 days. It records 186 hours of sunshine of sunshine.
Annual Temperatures in China Compared
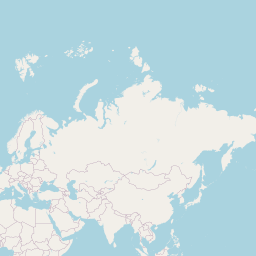
The map below shows the annual temperature across China. You can also select the different months in case you are interested in a specific month.
 very warm
very warm
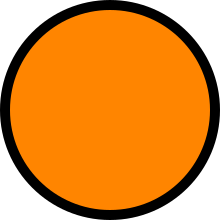 warm
warm
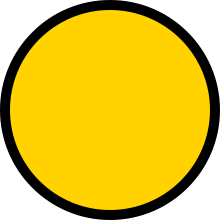 pleasant
pleasant
 moderate
moderate
 cold
cold
 very cold
very cold
Beijing Temperatures Compared World Wide
Beijing’s average annual maximum temperature is 20°C. Let’s compare this with some popular tourist destinations:
Seville, Spain, stands out with its warm Mediterranean climate and an average annual temperature of 23°C.
Glasgow, Scotland, the average annual temperature is significantly lower at 13°C, with mild summers and cold winters.
Osaka, Japan, offers a similar climate to Tokyo, with an average annual temperature of 22°C.
In Brisbane, Australia, the average annual temperature is 26°C, making it warmer than Sydney.
How does the temperature feel?
Humidity is an essential factor in how you experience temperature. When a warm period is accompanied by high humidity, it results in a higher perceived temperature. This is especially true when temperatures exceed 25°C, as it can cause greater discomfort.
On the other hand, in cooler months, especially when temperatures dip below 10°C, high humidity can intensify the cold. This makes the air feel much colder than it really is.
In Beijing, during the coolest month, January, you will experience 44% humidity, which is considered moderate. This is accompanied by an average maximum temperature of 3°C. In the warmest month, July, the humidity is 70% combined with an average maximum temperature of 34°C, which creates a high-feel temperature. Explore our detailed page on humidity levels for further details.
How are these Temperatures Measured?
Generally, temperature data depicting climate is usually given over a 30-year average in order to reduce short-term fluctuations and reveal better long-term trends in climate conditions.
This temperature data is taken from land-based thermometers, ocean buoys, ships, and satellites. These measurements are transmitted to weather stations and climate centers around the globe where they are processed, averaged, and analyzed in order to monitor the trends and create climate models.
Temperatures in the Mountains
Although not all regions have mountains, elevated areas exhibit distinct temperature variations.
- Sun Exposure: Sunlit slopes tend to be warmer, while shaded areas remain cooler.
- Altitude Effects: Temperatures drop by approximately 6°C for every 1,000 meters of elevation, creating distinct microclimates.
For more detailed information about Beijing’s weather, including monthly rainfall, sunshine hours, and humidity levels, visit our Beijing climate page.
Current temperature in Beijing